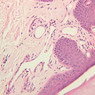
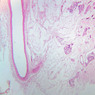
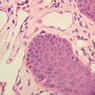
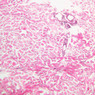
You are here: Medical Histology>Main Web>AtlasContents>CardiovascularSystemAtlas05 (19 Jun 2015, LorenEvey)Edit Attach
Chapter Five: Cardiovascular System
Introduction
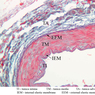
The cardiovascular system is composed of a pump, the heart, the arterial and venous tubes of varying diameters which conduct blood to and from the heart, and the lymphatic system which returns interstitial fluid to the heart. The essential work of the blood is to transfer nutritive substances and oxygen to the tissues and receiving waste products from them. This is accomplished in capillary or sinusoidal beds which almost always intervene between arteries and veins. Capillaries and sinusoids are tubes composed merely of endothelium and basal lamina. The walls of larger vessels and of the heart itself are structurally more complex and contain elements of all four primary tissues previously studied (i.e. epithelium, connective tissue, muscle and nerve). Vascular walls are composed of three layers or tunics: 1) tunica intima, the inner layer, consisting of an endothelial lining plus longitudinally oriented connective tissue elements; 2) tunica media, the middle layer, consisting of smooth muscle and connective tissue elements arranged in a circular or spiral fashion; and 3) tunica adventitia, the outer layer, consisting of connective tissue elements and some smooth muscle arranged longitudinally. The larger vessels are well supplied with nerves (to control the media musculature), blood vessels and lymphatics, distributed largely in the adventitia. These layers are present in all blood vessels, however, the proportional size of the various layers differs in different types of vessels. You should be able to recognize the following: A. Tunica intima (or interna) - endothelium with its basement lamina. Internal elastic membrane (elastica interna, or internal elastic lamina) separates the intima from the media. B. Tunica media - circular or spirally arranged smooth muscle - may also possess some elastic fibers and some connective tissue. External elastic membrane (elastica externa, or external elastic lamina) separates media from the adventitia and is less conspicuous than the internal elastic membrane. C. Tunica adventitia - connective tissue, elastic fibers, and fibroblasts. Top of pageElastic Arteries
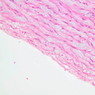
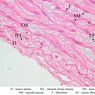
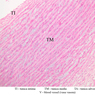
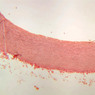
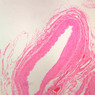
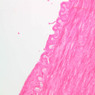
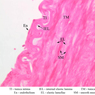
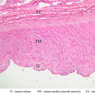
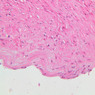
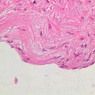
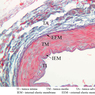
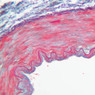
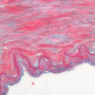
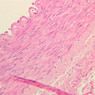
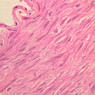
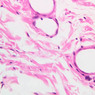
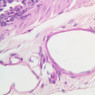
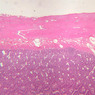
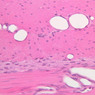
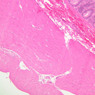
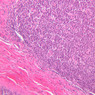
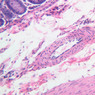
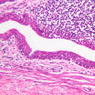
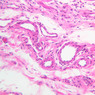
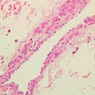
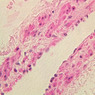
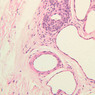
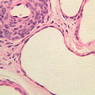
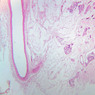
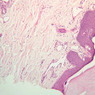
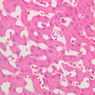
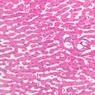
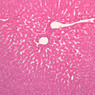
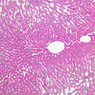
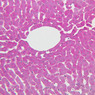
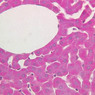
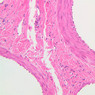
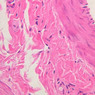
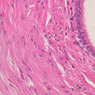
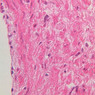
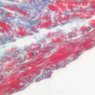
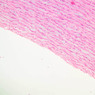
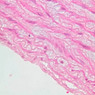
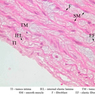
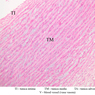
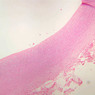
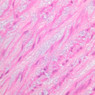
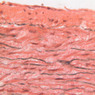
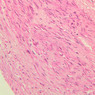
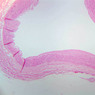
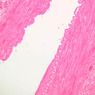
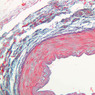
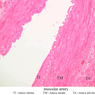
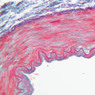
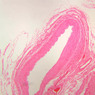
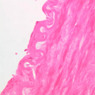
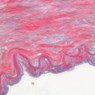
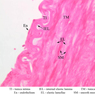
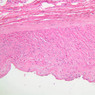
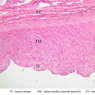
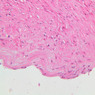
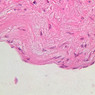
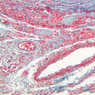
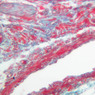
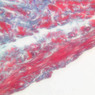
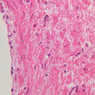
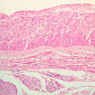
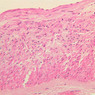
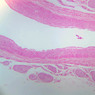
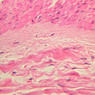
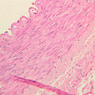
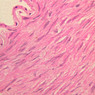
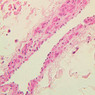
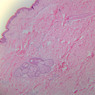
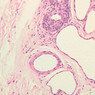
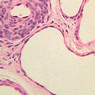
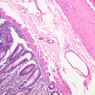
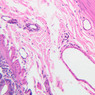
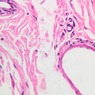
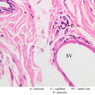
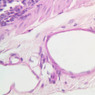
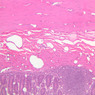
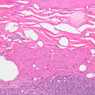
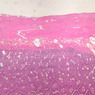
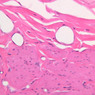
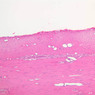
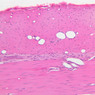
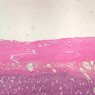
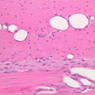
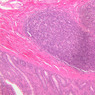
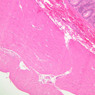
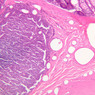
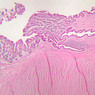
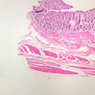
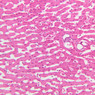
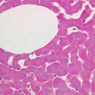
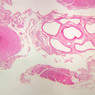
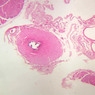
The blood is pumped from the heart into large, elastic (conduction) arteries. Examine a section of the aorta (A-26, H&E [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x-labeled] [2.5x, 10x-labeled, 20x, 40x]) which is a typical elastic artery. Although the tunica intima and tunica media are difficult to distinguish, note that together they are much thicker than the tunica adventitia. Using high power magnification, examine the tunica media and identify the cell types and fibers, recalling that elastic tissue appears light pink and refractive in H&E preparations. Compare this slide with a section of aorta stained to demonstrate elastic fibers (A-27, verhoeff [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x-labeled] [2.5x, 10x]). Note how extensive the elastic tissue is in the tunica media. The elastic tissue is arranged in the form of numerous concentric elastic lamellae, which are cross connected by slender elastic fibers. Observe the distribution of elastic fibers in the tunica intima (A- 27 [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x]) and tunica adventitia (A-27 [10x, 20x, 40x]). The internal and external elastic membranes are not well demarcated in the aorta since so many elastic lamellae are present. The elasticity of the aorta allows it to expand and absorb much of the pressure during contraction of the left ventricle (i.e., systole). When the ventricle relaxes (diastole), the elastic aorta contracts, continuing the movement of blood into the medium and muscular arteries.Elastic Artery Image Gallery
Elastic Artery of Identifications
| Row | Structure | Abbreviation | Optimal Stain | Representative Section | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tunica Intima | TI | H&E | |
|
| 2 | Tunica Media | TM | H&E | |
|
| 3 | Tunica Adventitia | TA | H&E | |
|
| 4 | Vasa Vasora (Blood Vessel) | V | H&E | |
|
| 5 | Internal Elastic Lamina | IEL | H&E | |
|
| 6 | Smooth Muscle | SM | H&E | |
|
| 7 | Fibroblast | F | H&E | |
|
| 8 | Elastic Fiber | EF | H&E | |
|
| 9 | Endothelium | En | Verhoeff | |
|
| 10 | Elastic Lamellae | EL | Verhoeff | |
Top of page
Muscular Arteries
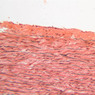
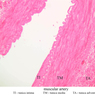
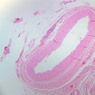
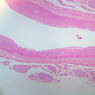
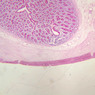
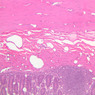
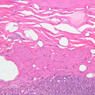
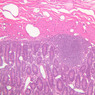
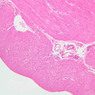
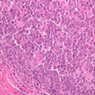
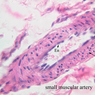
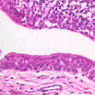
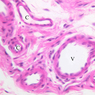
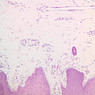
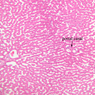
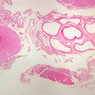
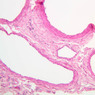
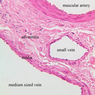
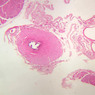
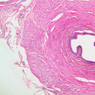
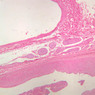
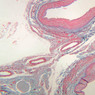
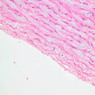
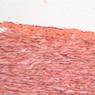
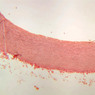
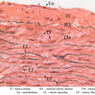
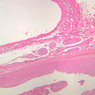
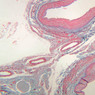
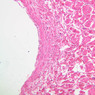
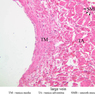
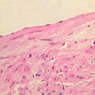
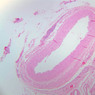
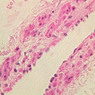
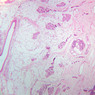
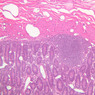
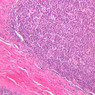
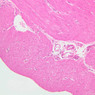
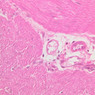
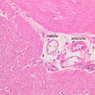
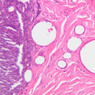
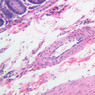
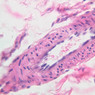
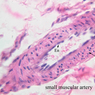
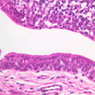
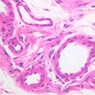
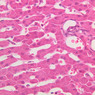
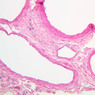
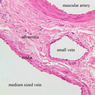
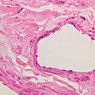
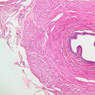
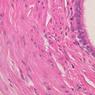
Blood passes from the elastic arteries via arteries of intermediate type into the muscular (distribution) arteries. Locate and examine a muscular artery in slide A-28 (Renal artery & vein, H&E [2.5x, 10x-labeled, 20x, 40x-labeled] [10x-labeled, 20x, 40x]; AF [10x-labeled, 20x, 40x]). Note that the tunica intima is separated from the tunica media by a thick internal elastic membrane which has a scalloped appearance. The tunica media consists of many layers of smooth muscle cells arranged concentrically in a spiral fashion (A-28, H&E [2.5x, 10x-labeled, 20x, 40x] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x, 40x] [2.5x, 10x, 20x]). An external elastic membrane is present, but is thinner and less complete than the internal elastic membrane. The tunica adventitia is about equal in size to the media in this vessel and is more intensely eosinophilic in its staining properties. Note the appearance of small blood vessels in the outer part of the tunica adventitia. You may also be able to see occasional nerve fibers.Muscular Artery Image Gallery
Muscular Artery Table of Identifications
| Row | Structure | Abbreviation | Optimal Stain | Representative Section | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tunica Intima | TI | H&E, AF | |
|
| 2 | Tunica Media | TM | H&E, AF | |
|
| 3 | Tunica Adventitia | TA | H&E, AF | |
|
| 4 | Internal Elastic Membrane | IEM | AF | |
|
| 5 | External Elastic Membrane | EEM | AF | |
|
| 6 | Smooth Muscle | SM | H&E | |
|
| 7 | Nerve | N | H&E | |
|
| 8 | Endothelium | En | H&E | |
|
| 9 | Elastic Lamellae | EL | H&E | |
|
| 10 | Internal Elastic Lamina | IEL | H&E | |
Top of page
The Terminal Vascular Bed
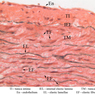
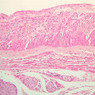
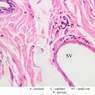
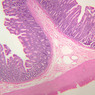
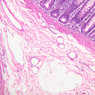
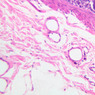
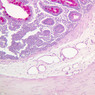
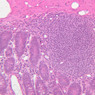
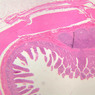
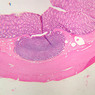
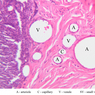
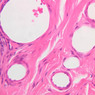
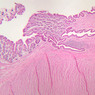
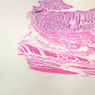
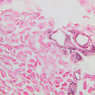
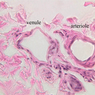
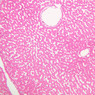
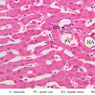
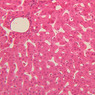
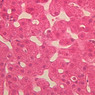
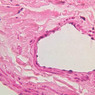
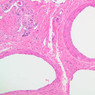
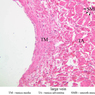
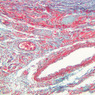
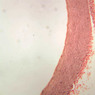
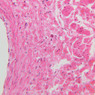
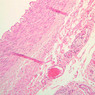
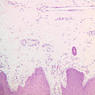
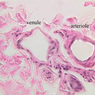
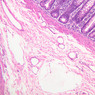
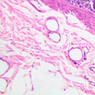
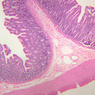
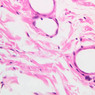
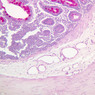
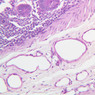
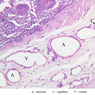
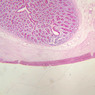
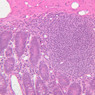
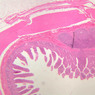
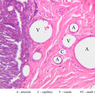
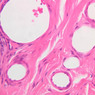
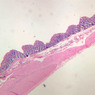
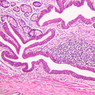
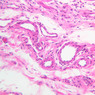
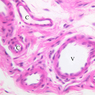
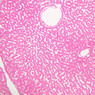
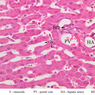
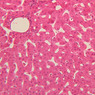
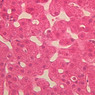
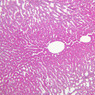
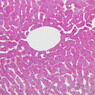
Arterioles, capillaries, sinusoids, and venules comprise the terminal vascular bed. The larger arterioles, having a diameter of 100 μm or less, consist of endothelium, an incomplete internal elastic membrane, one to three layers of smooth muscle cells, and some connective tissue. As the arterioles decrease in diameter, the amount of smooth muscle in the tunica media also decreases. The internal elastic membrane disappears and the tunica adventitia is reduced to a few collagen fibers and fibroblasts. Vessels of this type pass into true capillaries, which are merely endothelial tubes about 7-10 μm in diameter, surrounded by a few reticular fibers and variable numbers of pericytes. Two types of capillaries can be recognized by electron microscopy. Continuous capillaries consist of a sheet of endothelial cells that, as the name implies, has no defects or discontinuities. Fenestrated capillaries have areas of fusion of plasmalemmae that are responsible for enhanced transport as in kidney and endocrine organs. Discontinuous capillaries, or sinusoids, have gaps between individual endothelial cells. Sinusoids of the liver and spleen are examples. Sinusoids, which occur in some organs as branches directly from arterioles (in place of capillaries) also consist of a single layer of endothelial cells, but are two to three times greater in diameter and more irregular in shape than capillaries. Many of the cells lining sinusoids have phagocytic capabilities (e.g. Kupffer cells of the liver). Venules, the vessels into which capillaries or sinusoids feed and the smallest vessels of the venous system are endothelial tubes, larger in diameter than capillaries, surrounded by a thin sheath of connective tissue cells and fibers. When venules reach a diameter of about 40 μmμ, smooth muscle cells appear, but do not form a distinct layer. Look for arterioles, capillaries, and venules in slides B-12 (jejunum, H&E [10x, 20x, 40x-labeled] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x]), B-13 (jejunum, PAS [2.5x, 10x, 20x-labeled, 40x]), B-15 (jejunum, H&E [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x] [10x, 20x, 40x]), B-16 (ileum, H&E [10x, 20x, 40x-labeled] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x]), B-23 (colon, H&E [2.5x, 10x, 20x-labeled, 40x]), B-24 (colon, H&E [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x-labeled]), B-26 (rectal-anal junction, H&E [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x-labeled]). Capillaries and venules may be distinguished from small lymph vessels, also present, by the fact that the blood vessels contain red blood cells while the lymph vessels do not. Study a number of examples of each kind of small vessel, looking for the changes that characterize arterioles as they get smaller and venules as they get larger. Be able to distinguish differences between capillaries and the smallest arterioles and venules. Look for additional examples of small vessels of the various kinds in the dense connective tissue of skin (A-48, abdominal [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x]; A-50, fingertip [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x]; A-58, axillary [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x-labeled]), using care not to confuse the cross-sections of glands (which consist almost entirely of epithelial cells) with blood vessels. Arterioles, especially, are cut in different planes and are not always easy to identify. The structure of sinusoids can be studied in the liver (B-29, H&E [10x, 20x, 40x] [10x-labeled, 20x, 40x-labeled]; B-30, H&E [10x, 20x, 40x]; B-35, PAS [10x, 20x, 40x]) where they occur as endothelial tubes between plates of hepatocytes. In the liver, they are channels slightly larger in diameter than red blood cells and the individual lining cells have open spaces between them. The principal difference between sinusoids and capillaries is size, which presumably allows blood to flow more slowly in the larger sinusoids.Terminal Vascular Bed Image Gallery
Terminal Vascular Bed Table of Identifications
| Row | Structure | Abbreviation | Optimal Stain | Representative Section | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Central Vein | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 2 | Portal Canal | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 3 | Sinusoids | S | H&E | |
|
| 4 | Portal Vein | PV | H&E | |
|
| 5 | Hepatic Artery | HA | H&E | |
|
| 6 | Bile Duct | BD | H&E | |
|
| 7 | Arteriole | A | PAS, H&E | |
|
| 8 | Capillary | C | PAS, H&E | |
|
| 9 | Venule | V | PAS, H&E | |
|
| 10 | Small Vein | SV | H&E | |
|
| 11 | Pericyte | P | H&E | |
|
| 12 | Endothelial Cell | En | H&E | |
|
| 13 | Smooth Muscle | SM | H&E | |
Top of page
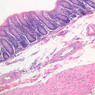
Veins
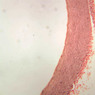
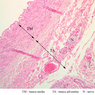
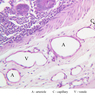
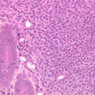
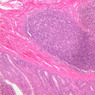
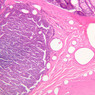
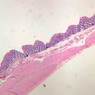
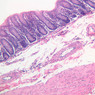
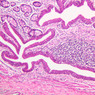
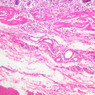
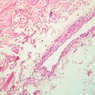
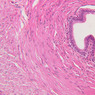
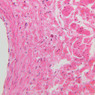
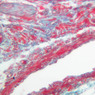
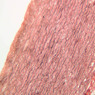
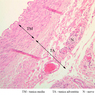
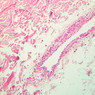
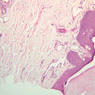
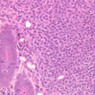
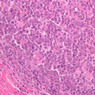
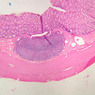
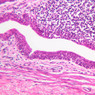
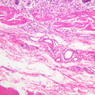
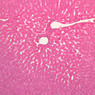
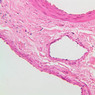
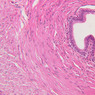
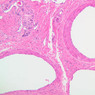
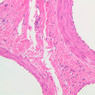
Veins are generally divided into small, medium, and large categories, though this division is not as readily based upon structural differences as among arteries. Examine a section of medium-sized vein (B-83, spermatic cord [2.5x, 10x, 20x-labeled, 40x] [10x, 20x, 40x] [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x]). The tunica adventitia, composed mainly of collagenous fibers cut obliquely or transversely, may be the thickest of the three coats. A thin internal elastic membrane can be seen in places around the vessel, but it is much less prominent than the membrane of the companion artery. No external elastic membrane is distinguishable in the vein. Compare the features of artery and vein: thickness of wall, size of lumen, amount of musculature, etc. The vein has a relatively wide lumen and a thin wall because it carries large volumes of blood at low pressures. Large veins have a very narrow tunica intima and only a few layers of muscle and fibers in the tunica media (A-28, H&E [2.5x, 10x-labeled, 20x, 40x], AF [2.5x, 10x, 20x, 40x]). Its chief coat, as in smaller veins, is the tunica adventitia, but in this case, the coat is composed mostly of longitudinal muscle fibers. Some other large veins, particularly those of the cranial cavity, lack muscle and thus differ from the venae cavae. The structure of veins generally and large veins in particular is more variable than arterial structure.Veins Image Gallery
Veins Table of Identifications
| Row | Structure | Abbreviation | Optimal Stain | Representative Section | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Large Vein | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 2 | Tunica Media | TM | H&E | |
|
| 3 | Tunica Adventitia | TA | H&E | |
|
| 4 | Smooth Muscle Bundles | SMB | H&E | |
|
| 5 | Medium Vein | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 6 | Small Vein | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 7 | Muscular Artery | (none) | H&E | |
Top of page
Chapter Five Review
Review of Slides
Review of Identifications
| Row | Structure | Abbreviation | Optimal Stain | Representative Section | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tunica Intima | TI | H&E, AF | |
|
| 2 | Tunica Media | TM | H&E, AF | |
|
| 3 | Tunica Adventitia | TA | H&E, AF | |
|
| 4 | Vasa Vasora (Blood Vessel) | V | H&E | |
|
| 5 | Internal Elastic Lamina | IEL | H&E | |
|
| 6 | Smooth Muscle | SM | H&E | |
|
| 7 | Fibroblast | F | H&E | |
|
| 8 | Elastic Fiber | EF | H&E | |
|
| 9 | Endothelium | En | Verhoeff | |
|
| 10 | Elastic Lamellae | EL | Verhoeff | |
|
| 11 | Internal Elastic Membrane | IEM | AF | |
|
| 12 | External Elastic Membrane | EEM | AF | |
|
| 13 | Smooth Muscle | SM | H&E | |
|
| 14 | Nerve | N | H&E | |
|
| 15 | Endothelium | En | H&E | |
|
| 16 | Internal Elastic Lamina | IEL | H&E | |
|
| 17 | Central Vein | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 18 | Portal Canal | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 19 | Sinusoids | S | H&E | |
|
| 20 | Portal Vein | PV | H&E | |
|
| 21 | Hepatic Artery | HA | H&E | |
|
| 22 | Bile Duct | BD | H&E | |
|
| 23 | Arteriole | A | PAS, H&E | |
|
| 24 | Capillary | C | PAS, H&E | |
|
| 25 | Venule | V | PAS, H&E | |
|
| 26 | Small Vein | SV | H&E | |
|
| 27 | Pericyte | P | H&E | |
|
| 28 | Endothelial Cell | En | H&E | |
|
| 29 | Large Vein | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 30 | Smooth Muscle Bundles | SMB | H&E | |
|
| 31 | Medium Vein | (none) | H&E | |
|
| 32 | Muscular Artery | (none) | H&E | |
Top of page
Comments
Top of page -- AshleyLPistorio - 27 May 2007Edit | Attach | Print version | History: r2 < r1 | Backlinks | View wiki text | More topic actions
Topic revision: r2 - 19 Jun 2015, LorenEvey
- Epithelium
- Connective Tissue
- Muscle
- Nervous Tissue
- Cardiovascular System
- Skin Appendages and Sensory Receptors
- Lymphatic System
- Cartilage and Bone
- Respiratory System
- Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow
- Oral Cavity and Salivary Glands
- Esophagus and Gastrointestinal Tract
- Pancreas, Liver, and Gall Bladder
- Endocrine Organs
- Male Reproductive System
- Female Reproductive System
- Urinary System
 Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors.
Copyright © by the contributing authors. All material on this collaboration platform is the property of the contributing authors. Ideas, requests, problems regarding Medical Histology? Send feedback